(SSTattler: Many YouTube's about Swallowing (Dysphagia). This article has 12 YouTube's, 3 YouTube's at the first and 9 more if you want it - just click "Read more --->>". They will show Swallowing Disorders, Thicken Liquids, Diet, Young Adult, Gastrostomy Tube and Nasogastric Tube. The swallowing topic is complex -- maybe I will tackle in another Saturday News/YouTube with a sub-topic of swallowing later).
Dysphagia From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
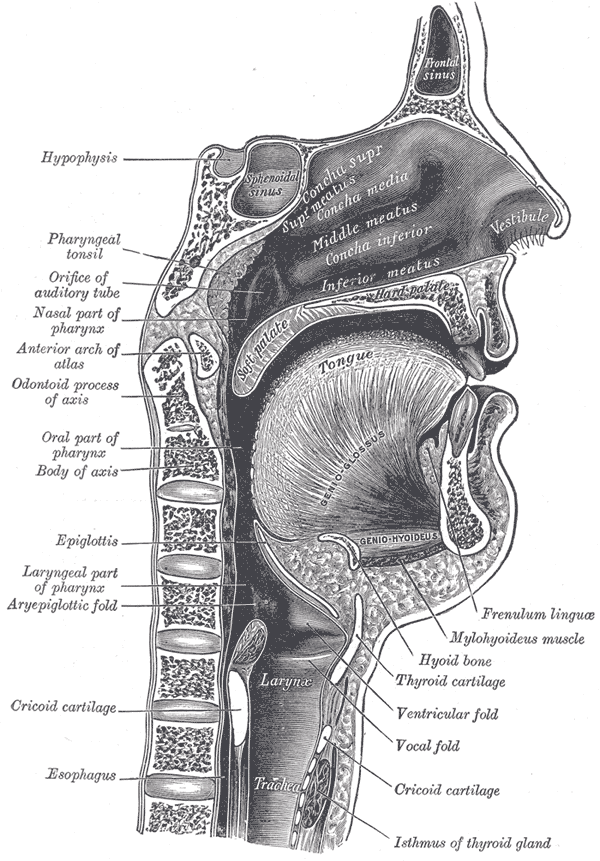
Dysphagia is the medical term for the symptom of difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, the term is sometimes used as a condition in its own right. Sufferers are sometimes unaware of their dysphagia.
It is derived from the Greek dys meaning bad or disordered, and phago meaning "eat". It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liquids from the mouth to the stomach, a lack of pharyngeal sensation, or various other inadequacies of the swallowing mechanism. Dysphagia is distinguished from other symptoms including odynophagia, which is defined as painful swallowing, and globus, which is the sensation of a lump in the throat. A psychogenic dysphagia is known as phagophobia.
It is also worthwhile to refer to the physiology of swallowing in understanding dysphagia.
Some patients have limited awareness of their dysphagia, so lack of the symptom does not exclude an underlying disease. When dysphagia goes undiagnosed or untreated, patients are at a high risk of pulmonary aspiration and subsequent aspiration pneumonia secondary to food or liquids going the wrong way into the lungs. Some people present with "silent aspiration" and do not cough or show outward signs of aspiration. Undiagnosed dysphagia can also result in dehydration, malnutrition, and renal failure.
Some signs and symptoms of oropharyngeal dysphagia include difficulty controlling food in the mouth, inability to control food or saliva in the mouth, difficulty initiating a swallow, coughing, choking, frequent pneumonia, unexplained weight loss, gurgly or wet voice after swallowing, nasal regurgitation, and dysphagia (patient complaint of swallowing difficulty). When asked where the food is getting stuck, patients will often point to the cervical (neck) region as the site of the obstruction. The actual site of obstruction is always at or below the level at which the level of obstruction is perceived.
The most common symptom of esophageal dysphagia is the inability to swallow solid food, which the patient will describe as 'becoming stuck' or 'held up' before it either passes into the stomach or is regurgitated.
Pain on swallowing or odynophagia is a distinctive symptom that can be highly indicative of carcinoma, although it also has numerous other causes that are not related to cancer.
Achalasia is a major exception to usual pattern of dysphagia in that swallowing of fluid tends to cause more difficulty than swallowing solids. In achalasia, there is idiopathic destruction of parasympathetic ganglia of the auerbach submucosal plexus of the entire esophagus, which results in functional narrowing of the lower esophagus, and peristaltic failure throughout its length.
Dysphagia is classified into two major types:
- oropharyngeal dysphagia and
- esophageal dysphagia.
- Functional dysphagia is defined in some patients as having no organic cause for dysphagia that can be found.
- Cerebrovascular Stroke ...
See also Swallowing From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Normal Swallow Tutorial with Modified Barium Swallow
http://www.FauquierENT.net - This video shows what happens when a person swallows from an X-ray as well as endoscopic view. To best illustrate what is going on, a modified barium swallow study is shown. NO REAL PATIENTS IN THIS VIDEO. ACTORS WERE USED. Read more about swallowing problems here here Ear, Nose & Throat Consultants.Understanding Dysphagia
Dr. Steven Feinberg Discusses Swallowing Disorders
Dysphagia - How to thicken liquids with Resource ThickenUp Clear
With Resource® ThickenUp Clear, Nestlé has developed an innovative thickening agent which rapidly achieves and maintains a stable bolus viscosity in all types of liquids.
Resource® ThickenUp Clear dissolves fully and easily without creating lumps in all types of liquids, including oral nutritional supplements. With this innovative thickening agent, the swallow-safe bolus is easier than ever to achieve, as the same dosage works for all liquids for a required thickening level.
The Benefits of Resource® ThickenUp Clear:
- is fully transparent in water and does not affect color in other liquids
- remains consistent over time; no overthickening
- is free of lumps in all types of liquids
- is odorless and tasteless and visually more appetizing
- is easily applicable in a wide variety of liquids, including hot or cold, protein-containing or acidic beverages
- requires the same dosage for all liquids for a given thickening level
- rapidly achieves a stable and appropriate consistency
- is resistant to salivary amylase; no thinning over time
Dysphagia - The Pureed Diet Made Easy
Reviews the process of pureeing and serving attractive pureed foods. Allowed and avoided food are discussed.See also How To Eat When You Can't Swallow
Looking for a guide on How To Eat When You Can't Swallow? This useful tutorial explains accurately how it's done, and will help you get good at throat problems. Enjoy this educational resource from the world's most comprehensive library of free factual video content online.Dysphagia after stroke in a young adult.
A sample clip from the DVD - Dysphagia: Experiences of people with swallowing difficulties. Andrew describes his swallowing difficulties after a cerebellum stroke. He has largely recovered his swallow. The DVD is now available from NL Productions. E-mail: ian.nlproductions@gmail.com or go to http://www.nlproductionsuk.co.uk/page4/page4.html for details.Gastrostomy Tube Overview
For more information, visit CancerQuest at http://www.cancerquest.org/gastrostomy-cd.An animation depicting the use of a gastrostomy (G) tube. It is part of an education series developed by CancerQuest. G tubes are also called PEG tubes, feeding tubes or stomach tubes. For further information, visit http://www.cancerquest.org
Gastrostomy - Feeding Tube Components
Consultant Paediatric Surgeon Mr. David Crabbe describes the feeding tube components, the gastrostomy operation and the fitting of a PEG button. This is a short clip from a full interview on NL Productions UK's DVD: Gastrostomy Feeding: Experiences of parent carers and adults using nutritional support. The full version contains images and illustrations of surgical procedures. Go to http://www.nlproductionsuk.co.uk/page3/page3.html for details.Reasons for a Gastrostomy
Consultant Paediatric Surgeon Mr. David Crabbe outlines the discussions he has with parents prior to a possible gastrostomy operation and the advantages of a gastrostomy for children and those with a physical handicap. He describes the common types of problems encountered with gastrostomies and adds a brief description of the feeding tube. This is a short clip from a full interview on NL Productions UK's DVD: Gastrostomy Feeding: Experiences of parent carers and adults using nutritional support.Go to http://www.nlproductionsuk.co.uk/page3/page3.html for details.



No comments:
Post a Comment